Secure communication (explained)
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is an extension of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) for secure communication over a computer network. In HTTPS, the communication protocol is encrypted using Transport Layer Security (TLS), or its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL).
In XProtect VMS, secure communication is obtained by using TLS/SSL with asymmetric encryption (RSA).
TLS/SSL uses a pair of keys—one private, one public—to authenticate, secure, and manage secure connections.
A certificate authority (CA) is anyone who can issue root certificates. This can be an internet service that issues root certificates, or anyone who manually generates and distributes a certificate. A CA can issue certificates to web services, that is to any software using https communication. This certificate contains two keys, a private key and a public key. The public key is installed on the clients of a web service (service clients) by installing a public certificate. The private key is used for signing server certificates that must be installed on the server. Whenever a service client calls the web service, the web service sends the server certificate, including the public key, to the client. The service client can validate the server certificate using the already installed public CA certificate. The client and the server can now use the public and private server certificates to exchange a secret key and thereby establish a secure TLS/SSL connection.
For manually distributed certificates, certificates must be installed before the client can make such a verification.
See Transport Layer Security for more information about TLS.
Certificates have an expiry date. XProtect VMS will not warn you when a certificate is about to expire. If a certificate expires:
• The clients will no longer trust the recording server with the expired certificate and thus cannot communicate with it
• The recording servers will no longer trust the management server with the expired certificate and thus cannot communicate with it
• The mobile devices will no longer trust the mobile server with the expired certificate and thus cannot communicate with it
To renew the certificates, follow the steps in this guide as you did when you created certificates.
Management server encryption (explained)
You can encrypt the two-way connection between the management server and the recording server. When you enable encryption on the management server, it applies to connections from all the recording servers that connect to the management server. If you enable encryption on the management server, you must also enable encryption on all of the recording servers. Before you enable encryption, you must install security certificates on the management server and all recording servers.
Certificate distribution for management servers
The graphic illustrates the basic concept of how certificates are signed, trusted, and distributed in XProtect VMS to secure the communication to the management server.

 A CA certificate acts as a trusted third party, trusted by both the subject/owner (management server) and by the party that verifies the certificate (recording servers)
A CA certificate acts as a trusted third party, trusted by both the subject/owner (management server) and by the party that verifies the certificate (recording servers)
 The CA certificate must be trusted on all recording servers. In this way, the recording servers can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA
The CA certificate must be trusted on all recording servers. In this way, the recording servers can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA
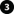 The CA certificate is used to establish a secure connection between the management server and the recording servers
The CA certificate is used to establish a secure connection between the management server and the recording servers
 The CA certificate must be installed on the computer on which the management server is running
The CA certificate must be installed on the computer on which the management server is running
Requirements for the private management server certificate:
- Issued to the management server so that the management server's host name is included in the certificate, either as subject (owner) or in the list of DNS names that the certificate is issued to
- Trusted on the management server itself, by trusting the CA certificate that was used to issue the management server certificate
- Trusted on all recording servers connected to the management server by trusting the CA certificate that was used to issue the management server certificate
Recording server data encryption (explained)
Encryption to clients and servers that retrieve data from the recording server
When you enable encryption on a recording server, communication to all clients, servers, and integrations that retrieve data streams from the recording server are encrypted. In this document referred to as 'clients':
- XProtect Smart Client
- Management Client
- Management Server (for System Monitor and for images and AVI video clips in email notifications)
- XProtect Mobile Server
- XProtect Event Server
- XProtect LPR
- Milestone Open Network Bridge
- XProtect DLNA Server
- Sites that retrieve data streams from the recording server through Milestone Interconnect
- Some third-party MIP SDK integrations
Certificate distribution
The graphic illustrates the basic concept of how certificates are signed, trusted, and distributed in XProtect VMS to secure the communication to the recording server.
 A CA certificate acts as a trusted third-party, trusted by both the Subject/owner (recording server) and by the party that verify the certificate (clients)
A CA certificate acts as a trusted third-party, trusted by both the Subject/owner (recording server) and by the party that verify the certificate (clients)
 The public CA certificate must be trusted on all client computers. In this way the clients can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA
The public CA certificate must be trusted on all client computers. In this way the clients can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA
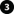 The CA certificate is used to issue private server authentication certificates to the recording servers
The CA certificate is used to issue private server authentication certificates to the recording servers
 The created private recording server certificates must be imported to the Windows Certificate Store on all recording servers
The created private recording server certificates must be imported to the Windows Certificate Store on all recording servers
Requirements for the private recording server certificate:
- Issued to the recording server so that the recording server's host name is included in the certificate, either as subject (owner) or in the list of DNS names that the certificate is issued to
- Trusted on all computers running services that retrieve data streams from the recording servers, by trusting the CA certificate that was used to issue the recording server certificate
- The service account that runs the recording server must have access to the private key of the certificate on the recording server.
If you enable encryption on the recording servers and your system applies failover recording servers, Milestone recommends that you also prepare the failover recording servers for encryption.
Encryption from the management server
You can encrypt the two-way connection between the management server and the recording server. When you enable encryption on the management server, it applies to connections from all the recording servers that connect to the management server. Therefore, you need to enable encryption on all the recording servers. Before you enable encryption, you must install security certificates on the management server and all recording servers.
Certificate distribution
The graphic illustrates the basic concept of how certificates are signed, trusted, and distributed in XProtect VMS to secure the communication from the management server.
 A CA certificate acts as a trusted third party, trusted by both the Subject/owner (recording server) and by the party that verify the certificate (management server)
A CA certificate acts as a trusted third party, trusted by both the Subject/owner (recording server) and by the party that verify the certificate (management server)
 The public CA certificate must be trusted on the management server. In this way the management server can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA
The public CA certificate must be trusted on the management server. In this way the management server can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA
 The CA certificate is used to issue private server authentication certificates to the recording servers
The CA certificate is used to issue private server authentication certificates to the recording servers
 The created private recording server certificates must be imported to the Windows Certificate Store on the management server
The created private recording server certificates must be imported to the Windows Certificate Store on the management server
Requirements for the private recording server certificate:
- Issued to the recording server so that the recording server's host name is included in the certificate, either as subject (owner) or in the list of DNS names that the certificate is issued to
- Trusted on the management server, by trusting the CA certificate that was used to issue the recording server certificate
- The service account that runs the recording server must have access to the private key of the certificate on the recording server.
Mobile server data encryption (explained)
In XProtect VMS, encryption is enabled or disabled per mobile server. When you enable encryption on a mobile server, you will have the option to use encrypted communication with all clients, services, and integrations that retrieve data streams.
Certificate distribution for mobile servers
The graphic illustrates the basic concept of how certificates are signed, trusted, and distributed in XProtect VMS to secure the communication with the mobile server.
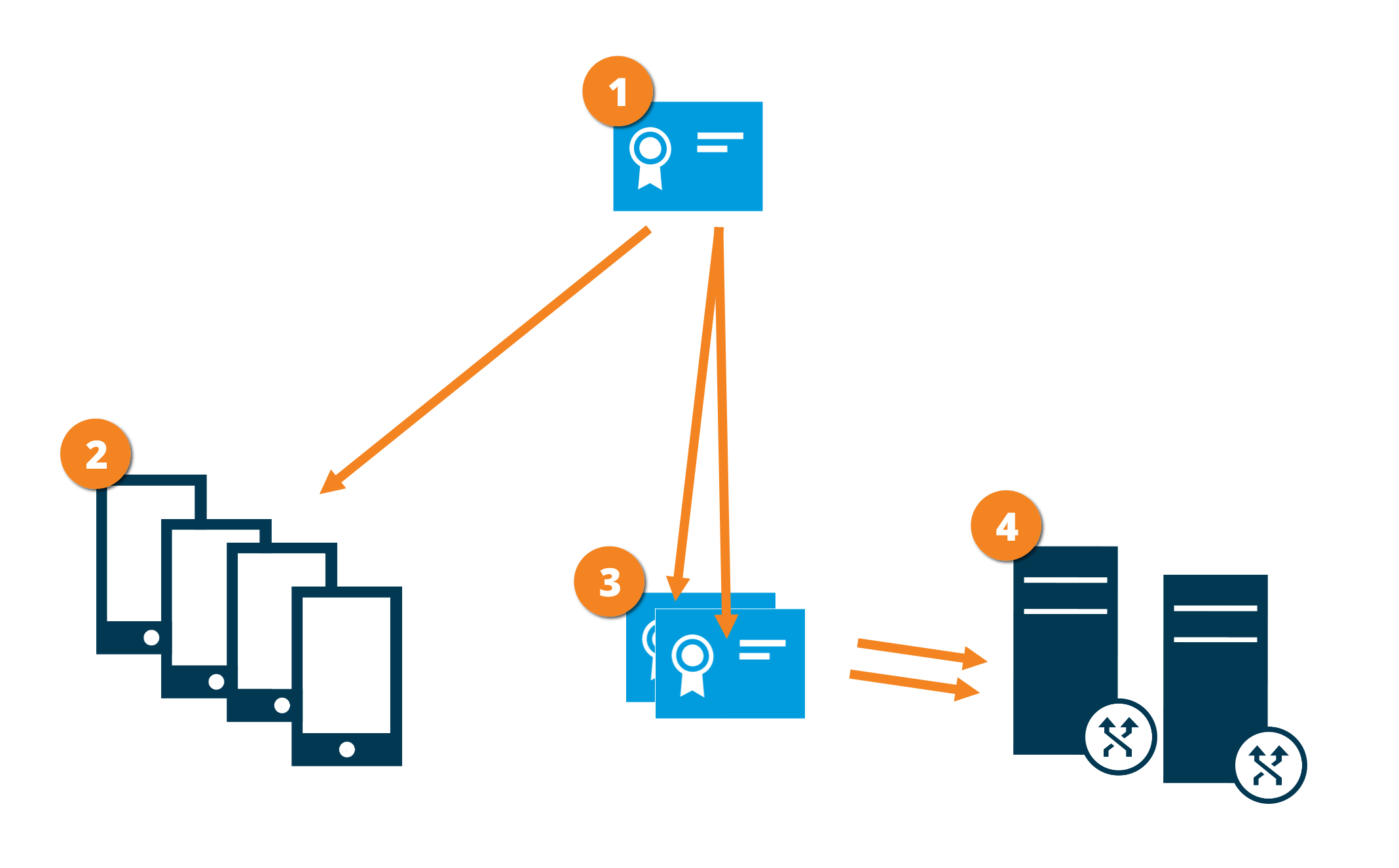
 A CA certificate acts as a trusted third party, trusted by both the subject/owner (mobile server) and by the party that verifies the certificate (all clients)
A CA certificate acts as a trusted third party, trusted by both the subject/owner (mobile server) and by the party that verifies the certificate (all clients)
 The CA certificate must be trusted on all clients. In this way, clients can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA
The CA certificate must be trusted on all clients. In this way, clients can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA
 The CA certificate is used to establish a secure connection between the mobile server and clients and services
The CA certificate is used to establish a secure connection between the mobile server and clients and services
 The CA certificate must be installed on the computer on which the mobile server is running
The CA certificate must be installed on the computer on which the mobile server is running
Requirements for the CA certificate:
- The mobile server's host name must be included in the certificate, either as subject/owner or in the list of DNS names that the certificate is issued to
- The certificate must be trusted on all devices that are running services that retrieve data streams from the mobile server
- The service account that runs the mobile server must have access to the private key of the CA certificate

