Encryption
This section gives you an introduction to encryption and certificates.
XProtect systems support secure communication:
|
From |
To |
|---|---|
| Recording Server |
Management Server |
| Management Server |
Recording Server |
| Clients, servers, and integrations that retrieve data streams from the recording server |
Recording Server |
| Mobile devices | Mobile Server |
| Management Server | Data Collector servers affiliated with remote servers |
| Data Collector servers affiliated with remote servers | Management Server |
When do you need to install certificates?
First, decide whether your system actually needs encrypted communication.
Don't use certificates with recording server encryption if you are using one or more integrations that don't support HTTPS communication. This is, for example, third-part MIP SDK integrations that don't support HTTPS.
Unless your installation is made in a physically isolated network, it's recommended that you secure the communication by using certificates.
This document describes when to use certificates:
- If your XProtect VMS system is set up in a Windows Workgroup environment
- Before you install or upgrade to XProtect VMS 2019 R1 or newer, if you want to enable encryption during the installation
- Before you enable encryption, if you installed XProtect VMS 2019 R1 or newer without encryption
- When you renew or replace certificates due to expiry
Introduction to certificates
El Protocolo de Transferencia de Hipertexto Seguro (HTTPS) es una extensión del Protocolo de Transferencia de Hipertexto (HTTP) para la comunicación segura a través de una red informática. En HTTPS, el protocolo de comunicación está cifrado mediante Transport Layer Security (TLS), o su predecesor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL).
En el VMS XProtect, la comunicación segura se obtiene utilizando TLS/SSL con cifrado asimétrico (RSA).
TLS/SSL utiliza un par de claves, una privada y otra pública, para autenticar, asegurar y gestionar las conexiones seguras.
Una autoridad de certificación (CA) es cualquiera que pueda emitir certificados raíz. Puede tratarse de un servicio de Internet que emita certificados raíz, o de cualquier persona que genere y distribuya manualmente un certificado. Una CA puede emitir certificados para servicios web, es decir, para cualquier software que utilice la comunicación https. Este certificado contiene dos claves, una clave privada y una clave pública. La clave pública se instala en los clientes de un servicio web (clientes del servicio) mediante la instalación de un certificado público. La clave privada se utiliza para firmar los certificados del servidor que deben instalarse en el mismo. Siempre que un cliente de servicio llama al servicio web, el servicio web envía el certificado del servidor, incluida la clave pública, al cliente. El cliente de servicio puede validar el certificado del servidor utilizando el certificado de CA público ya instalado. El cliente y el servidor pueden ahora utilizar los certificados público y privado del servidor para intercambiar una clave secreta y establecer así una conexión segura TLS/SSL.
Para los certificados distribuidos manualmente, los certificados deben ser instalados antes de que el cliente pueda realizar dicha verificación.
Vea Seguridad de capa de transporte para tener más información sobre TLS.
In XProtect VMS, the following locations are where you can enable TLS/SSL encryption:
- In the communication between the management server and the recording servers, event servers, and mobile servers
- On the recording server in the communication with clients, servers, and integrations that retrieve data streams from the recording server
- In the communication between clients and the mobile server
Certificate distribution
The graphic illustrates the basic concept of how certificates are signed, trusted, and distributed in XProtect VMS.
 A CA certificate acts as a trusted third-party, trusted by both the Subject/owner (server) and by the party that verifies the certificate (clients).
A CA certificate acts as a trusted third-party, trusted by both the Subject/owner (server) and by the party that verifies the certificate (clients).
 The public CA certificate must be trusted on all client computers. In this way the clients can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA.
The public CA certificate must be trusted on all client computers. In this way the clients can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA.
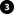 The CA certificate is used to issue private server authentication certificates to the servers.
The CA certificate is used to issue private server authentication certificates to the servers.
 The created private SSL certificates must be imported to the Windows Certificate Store on all servers.
The created private SSL certificates must be imported to the Windows Certificate Store on all servers.
Requirements for the private SSL certificate:
- Issued to the server so that the server's host name is included in the certificate, either as subject (owner) or in the list of DNS names that the certificate is issued to
- Trusted on all computers running services or applications that communicate with the service on the servers, by trusting the CA certificate that was used to issue the SSL certificate
- The service account that runs the server must have access to the private key of the certificate on the server.
Certificates have an expiry date. XProtect VMS will not warn you when a certificate is about to expire. If a certificate expires, the clients will no longer trust the server with the expired certificate and thus cannot communicate with it.
To renew the certificates, follow the steps in this guide as you did when you created certificates.
Si desea más información, consulte la guía de certificados sobre cómo asegurar sus instalaciones de XProtect VMS.


