Introduction to certificates
Протокол HTTPS является расширением протокола HTTP и обеспечивает безопасный обмен данными по сетям. В HTTPS шифрование протокола связи выполняется с помощью протокола TLS или его предшественника, SSL.
В VMS XProtect безопасный обмен данными реализуется за счет использования TLS/SSL с асимметричным шифрованием (RSA).
В протоколах TLS и SSL используется пара ключей (открытый и закрытый) для аутентификации, защиты и управления безопасными подключениями.
Центр сертификации (ЦС) ― это любое лицо, выдающее корневые сертификаты. Это может быть интернет-служба, выдающая корневые сертификаты, или любое лицо, вручную создающее и распространяющее сертификат. ЦС может выдавать сертификаты веб-службам, то есть любому ПО, использующему обмен данными по протоколу HTTPS. Этот сертификат содержит два ключа: открытый и закрытый. Открытый ключ устанавливается на клиентах веб-службы (клиенты службы) путем установки открытого сертификата. Закрытый ключ используется для подписывания сертификатов серверов, которые устанавливаются на сервере. Когда клиент службы вызывает веб-службу, веб-служба передает клиенту сертификат сервера, включая открытый ключ. Клиент службы может проверить сертификат сервера, используя уже установленный открытый сертификат ЦС. На этом этапе клиент и сервер могут использовать открытый и закрытый сертификаты сервера для обмена секретным ключом и создания защищенного TLS/SSL-подключения.
Что касается сертификатов, распространяемых вручную, их необходимо установить до того, как клиент сможет проводить такую проверку.
Дополнительные сведения о протоколе TLS см. в разделе Transport Layer Security.
In XProtect VMS, the following locations are where you can enable TLS/SSL encryption:
- In the communication between the management server and the recording servers, event servers, and mobile servers
- On the recording server in the communication with clients, servers, and integrations that retrieve data streams from the recording server
- In the communication between clients and the mobile server
In this guide, the following are referred to as clients:
- XProtect Smart Client
- Management Client
- Management Server (for System Monitor and for images and AVI video clips in email notifications)
- XProtect Mobile Server
- XProtect Event Server
- XProtect LPR
- Milestone Open Network Bridge
- XProtect DLNA Server
- Sites that retrieve data streams from the recording server through Milestone Interconnect
- Third-party MIP SDK integrations that support HTTPS
- If the integrations are made using MIP SDK libraries, they need to be rebuilt with MIP SDK 2019 R1
- If the integrations communicate directly with the Recording Server APIs without using MIP SDK libraries, the integrators must add HTTPS support themselves
- If in doubt, ask your vendor who supplied the integration
Certificate distribution
The graphic illustrates the basic concept of how certificates are signed, trusted, and distributed in XProtect VMS.
 A certificate authority (CA) is anyone who can issue root certificates. A CA certificate acts as a trusted third-party, trusted by both the subject/owner (server) and by the party that verifies the certificate (clients) (see Create CA certificate).
A certificate authority (CA) is anyone who can issue root certificates. A CA certificate acts as a trusted third-party, trusted by both the subject/owner (server) and by the party that verifies the certificate (clients) (see Create CA certificate).
 The public certificate must be trusted on all client computers. In this way the clients can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA (see Install certificates on the clients).
The public certificate must be trusted on all client computers. In this way the clients can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA (see Install certificates on the clients).
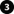 The CA certificate is used to issue private server authentication certificates to the servers (see Create SSL certificate).
The CA certificate is used to issue private server authentication certificates to the servers (see Create SSL certificate).
 The created private SSL certificates must be imported to the Windows Certificate Store on all servers (see Import SSL certificate).
The created private SSL certificates must be imported to the Windows Certificate Store on all servers (see Import SSL certificate).
Requirements for the private SSL certificate:
- Issued to the server so that the server's host name is included in the certificate, either as subject (owner) or in the list of DNS names that the certificate is issued to
- Trusted on all computers running services or applications that communicate with the service on the servers, by trusting the CA certificate that was used to issue the SSL certificate
- The service account that runs the server must have access to the private key of the certificate on the server.
Certificates have an expiry date. You will not receive a warning when a certificate is about to expire. If a certificate expires, the clients will no longer trust the server with the expired certificate and thus cannot communicate with it.
To renew the certificates, follow the steps in this guide as you did when you created certificates.