Introduction to certificates
하이퍼텍스트 전송 프로토콜 보안(Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure, HTTPS)은 하이퍼텍스트 전송 프로토콜(Hypertext Transfer Protocol, HTTP)의 연장으로 컴퓨터 네트워크 상의 보안 통신을 위한 것입니다. HTTPS에서 통신 프로토콜은 전송 레이어 보안(Transport Layer Security, TLS), 또는 그보다 먼저 나온 보안 소켓 레이어(Secure Sockets Layer, SSL)를 사용하여 암호화됩니다.
XProtect 비디오 관리 소프트웨어에서 비대칭 암호화(RSA)와 함께 TLS/SSL 프로토콜을 사용하여 안전하게 통신합니다.
TLS/SSL 프로토콜은 한 쌍의 키(하나는 개인 키, 하나는 공용 키)를 사용하여 보안 연결을 인증, 보호 및 관리합니다.
인증 권한(CA)은 루트 인증서를 발급할 수 있는 자입니다. 이는 루트 인증서를 발급할 수 있는 인터넷 서비스이거나 인증서를 수동으로 생성하고 배포하는 자일 수 있습니다. CA는 웹 서비스, 즉 https 통신을 사용하는 모든 소프트웨어에 대해 인증서를 발급할 수 있습니다. 이 인증서는 개인용 키 및 공공 키 2개를 포함합니다. 공개 키는 공개 인증서를 설치함으로써 웹 서비스의 클라이언트(서비스 클라이언트)에 설치됩니다. 개인 키는 서버에 설치되어있는 서명된 서버 인증서에 사용됩니다. 서비스 클라이언트가 웹 서비스를 호출할 때마다, 웹서비스는 공공 키를 포함한 서버 인증을 클라이언트에 전송합니다. 이미 설치된 공개 CA 인증서를 사용하여 서비스 클라이언트는 서버 인증서를 확인할 수 있습니다. 클라이언트와 서버는 이제 공개 및 개인 서버 인증서를 사용하여 비밀 키 교환 및 서버에서 보안 TLS/SSL 연결을 수립할 수 있습니다.
수동으로 배포된 인증서인 경우, 인증서는 클라이언트에서 확인하기 전에 설치되어야 합니다.
TLS에 대한 자세한 내용은 전송 계층 보안을 참조하십시오.
In XProtect VMS, the following locations are where you can enable TLS/SSL encryption:
- In the communication between the management server and the recording servers, event servers, and mobile servers
- On the recording server in the communication with clients, servers, and integrations that retrieve data streams from the recording server
- In the communication between clients and the mobile server
In this guide, the following are referred to as clients:
- XProtect Smart Client
- Management Client
- Management Server (for System Monitor and for images and AVI video clips in email notifications)
- XProtect Mobile Server
- XProtect Event Server
- XProtect LPR
- Milestone Open Network Bridge
- XProtect DLNA Server
- Sites that retrieve data streams from the recording server through Milestone Interconnect
- Third-party MIP SDK integrations that support HTTPS
- If the integrations are made using MIP SDK libraries, they need to be rebuilt with MIP SDK 2019 R1
- If the integrations communicate directly with the Recording Server APIs without using MIP SDK libraries, the integrators must add HTTPS support themselves
- If in doubt, ask your vendor who supplied the integration
Certificate distribution
The graphic illustrates the basic concept of how certificates are signed, trusted, and distributed in XProtect VMS.
 A certificate authority (CA) is anyone who can issue root certificates. A CA certificate acts as a trusted third-party, trusted by both the subject/owner (server) and by the party that verifies the certificate (clients) (see Create CA certificate).
A certificate authority (CA) is anyone who can issue root certificates. A CA certificate acts as a trusted third-party, trusted by both the subject/owner (server) and by the party that verifies the certificate (clients) (see Create CA certificate).
 The public certificate must be trusted on all client computers. In this way the clients can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA (see Install certificates on the clients).
The public certificate must be trusted on all client computers. In this way the clients can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA (see Install certificates on the clients).
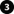 The CA certificate is used to issue private server authentication certificates to the servers (see Create SSL certificate).
The CA certificate is used to issue private server authentication certificates to the servers (see Create SSL certificate).
 The created private SSL certificates must be imported to the Windows Certificate Store on all servers (see Import SSL certificate).
The created private SSL certificates must be imported to the Windows Certificate Store on all servers (see Import SSL certificate).
Requirements for the private SSL certificate:
- Issued to the server so that the server's host name is included in the certificate, either as subject (owner) or in the list of DNS names that the certificate is issued to
- Trusted on all computers running services or applications that communicate with the service on the servers, by trusting the CA certificate that was used to issue the SSL certificate
- The service account that runs the server must have access to the private key of the certificate on the server.
Certificates have an expiry date. You will not receive a warning when a certificate is about to expire. If a certificate expires, the clients will no longer trust the server with the expired certificate and thus cannot communicate with it.
To renew the certificates, follow the steps in this guide as you did when you created certificates.