Secure communication (explained)
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) est une extension de Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) pour une communication sécurisée sur un réseau informatique. Sur HTTPS, le protocole de communication est crypté en utilisant Sécurité de la couche transport (TLS), ou son prédécesseur, Couche de sockets sécurisés (SSL).
Dans XProtect VMS, la communication sécurisée est obtenue en utilisant TLS/SSL avec un chiffrement asymétrique (RSA).
TLS/SSL utilise une paire de clés (une privée, une publique) pour authentifier, sécuriser et gérer les connexions sécurisées.
Une autorité de certification (AC) est toute personne capable d'émettre des certificats racine. Il peut s'agir d'un service Internet qui émet des certificats racine ou de toute personne qui génère manuellement et distribue un certificat. Une AC peut émettre des certificats aux services Web, c'est-à-dire à tout logiciel utilisant la communication https. Ce certificat contient deux clés, une clé privée et une clé publique. La clé publique est installée sur les clients d'un service Web (clients de service) en installant un certificat public. La clé privée est utilisée pour la signature des certificats de serveur qui doivent être installés sur le serveur. Lorsqu'un client de service appelle le service Web, le service Web envoie le certificat du serveur incluant la clé publique au client. Le client de service peut valider le certificat de serveur utilisant le certificat public de l'AC déjà installé. Le client et le serveur peuvent maintenant utiliser les certificats de serveur publics et privés pour échanger une clé secrète et par conséquent, établir une connexion TLS/SSL sécurisée.
Pour les certificats distribués manuellement, les certificats doivent être installés avant que le client ne puisse effectuer cette vérification.
Reportez-vous à la section Transport Layer Security pour plus d’informations concernant TLS.
Les certificats possèdent une date d’expiration. XProtect VMS ne vous préviendra pas lorsqu’un certificat est sur le point d’expirer. Si un certificat expire :
• Les clients ne feront plus confiance au serveur d’enregistrement dû au certificat expiré et ils ne pourront donc plus communiquer avec lui
• Les serveurs d’enregistrement ne feront plus confiance au serveur de gestion dû au certificat expiré et ne pourront donc plus communiquer avec lui
• Les périphériques mobiles ne feront plus confiance au serveur mobile dû au certificat expiré et ils ne pourront donc plus communiquer avec lui
Pour renouveler les certificats, suivez les étapes figurant dans ce guide que vous avez suivies lors de la création des lesdits certificats.
Management server encryption (explained)
You can encrypt the two-way connection between the management server and the recording server. When you enable encryption on the management server, it applies to connections from all the recording servers that connect to the management server. If you enable encryption on the management server, you must also enable encryption on all of the recording servers. Before you enable encryption, you must install security certificates on the management server and all recording servers.
Certificate distribution for management servers
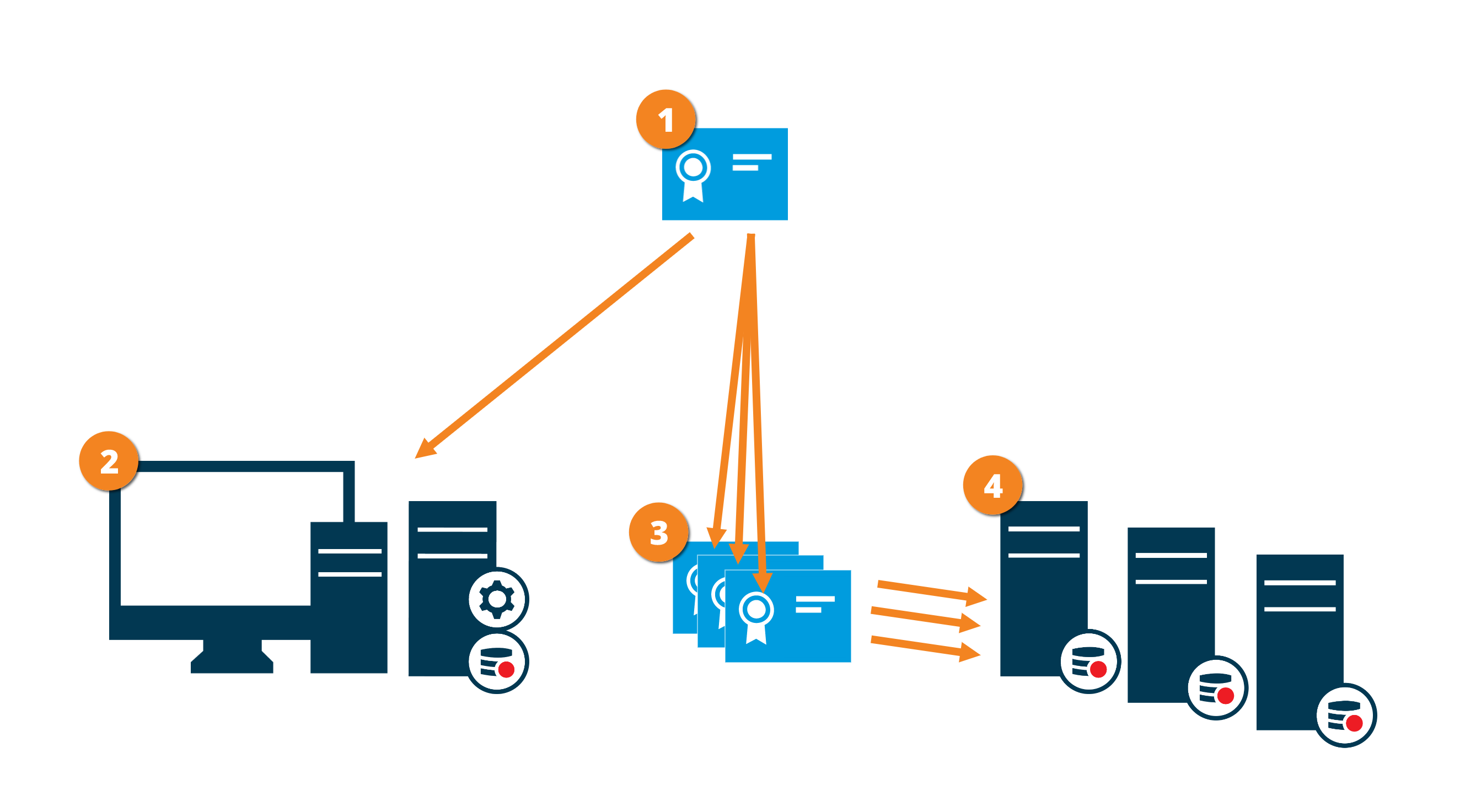
The graphic illustrates the basic concept of how certificates are signed, trusted, and distributed in XProtect VMS to secure the communication to the management server.
 A CA certificate acts as a trusted third party, trusted by both the subject/owner (management server) and by the party that verifies the certificate (recording servers)
A CA certificate acts as a trusted third party, trusted by both the subject/owner (management server) and by the party that verifies the certificate (recording servers)
 The CA certificate must be trusted on all recording servers. In this way, the recording servers can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA
The CA certificate must be trusted on all recording servers. In this way, the recording servers can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA
 The CA certificate is used to establish a secure connection between the management server and the recording servers
The CA certificate is used to establish a secure connection between the management server and the recording servers
 The CA certificate must be installed on the computer on which the management server is running
The CA certificate must be installed on the computer on which the management server is running
Requirements for the private management server certificate:
- Issued to the management server so that the management server's host name is included in the certificate, either as subject (owner) or in the list of DNS names that the certificate is issued to
- Trusted on the management server itself, by trusting the CA certificate that was used to issue the management server certificate
- Trusted on all recording servers connected to the management server by trusting the CA certificate that was used to issue the management server certificate
Recording server data encryption (explained)
Encryption to clients and servers that retrieve data from the recording server
When you enable encryption on a recording server, communication to all clients, servers, and integrations that retrieve data streams from the recording server are encrypted. In this document referred to as 'clients':
- XProtect Smart Client
- Management Client
- Management Server (for System Monitor and for images and AVI video clips in email notifications)
- XProtect Mobile Server
- XProtect Event Server
- XProtect LPR
- Milestone Open Network Bridge
- XProtect DLNA Server
- Sites that retrieve data streams from the recording server through Milestone Interconnect
- Some third-party MIP SDK integrations
Certificate distribution
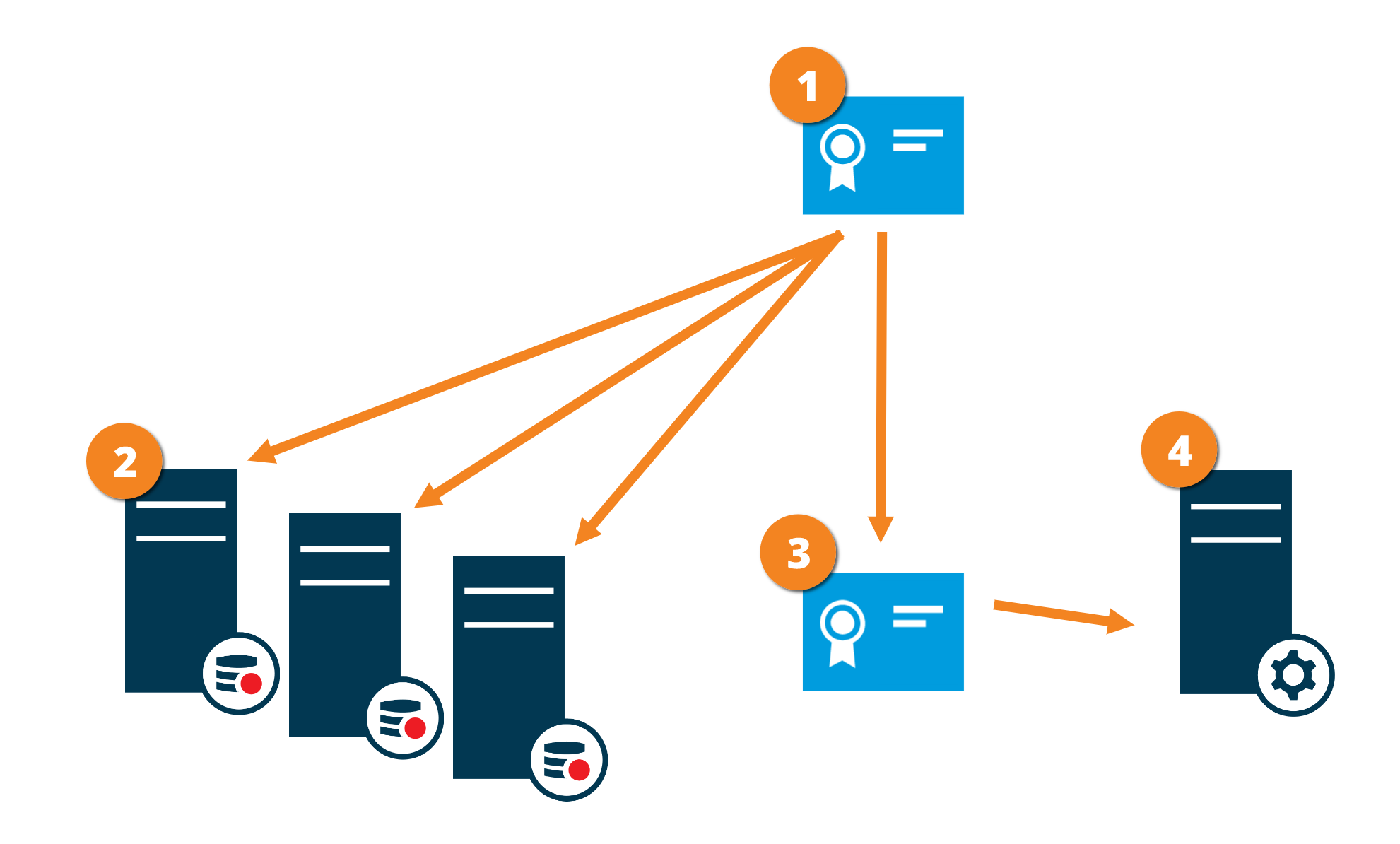
The graphic illustrates the basic concept of how certificates are signed, trusted, and distributed in XProtect VMS to secure the communication to the recording server.
 A CA certificate acts as a trusted third-party, trusted by both the Subject/owner (recording server) and by the party that verify the certificate (clients)
A CA certificate acts as a trusted third-party, trusted by both the Subject/owner (recording server) and by the party that verify the certificate (clients)
 The public CA certificate must be trusted on all client computers. In this way the clients can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA
The public CA certificate must be trusted on all client computers. In this way the clients can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA
 The CA certificate is used to issue private server authentication certificates to the recording servers
The CA certificate is used to issue private server authentication certificates to the recording servers
 The created private recording server certificates must be imported to the Windows Certificate Store on all recording servers
The created private recording server certificates must be imported to the Windows Certificate Store on all recording servers
Requirements for the private recording server certificate:
- Issued to the recording server so that the recording server's host name is included in the certificate, either as subject (owner) or in the list of DNS names that the certificate is issued to
- Trusted on all computers running services that retrieve data streams from the recording servers, by trusting the CA certificate that was used to issue the recording server certificate
- The service account that runs the recording server must have access to the private key of the certificate on the recording server.
If you enable encryption on the recording servers and your system applies failover recording servers, Milestone recommends that you also prepare the failover recording servers for encryption.
Encryption from the management server
You can encrypt the two-way connection between the management server and the recording server. When you enable encryption on the management server, it applies to connections from all the recording servers that connect to the management server. Therefore, you need to enable encryption on all the recording servers. Before you enable encryption, you must install security certificates on the management server and all recording servers.
Certificate distribution
The graphic illustrates the basic concept of how certificates are signed, trusted, and distributed in XProtect VMS to secure the communication from the management server.
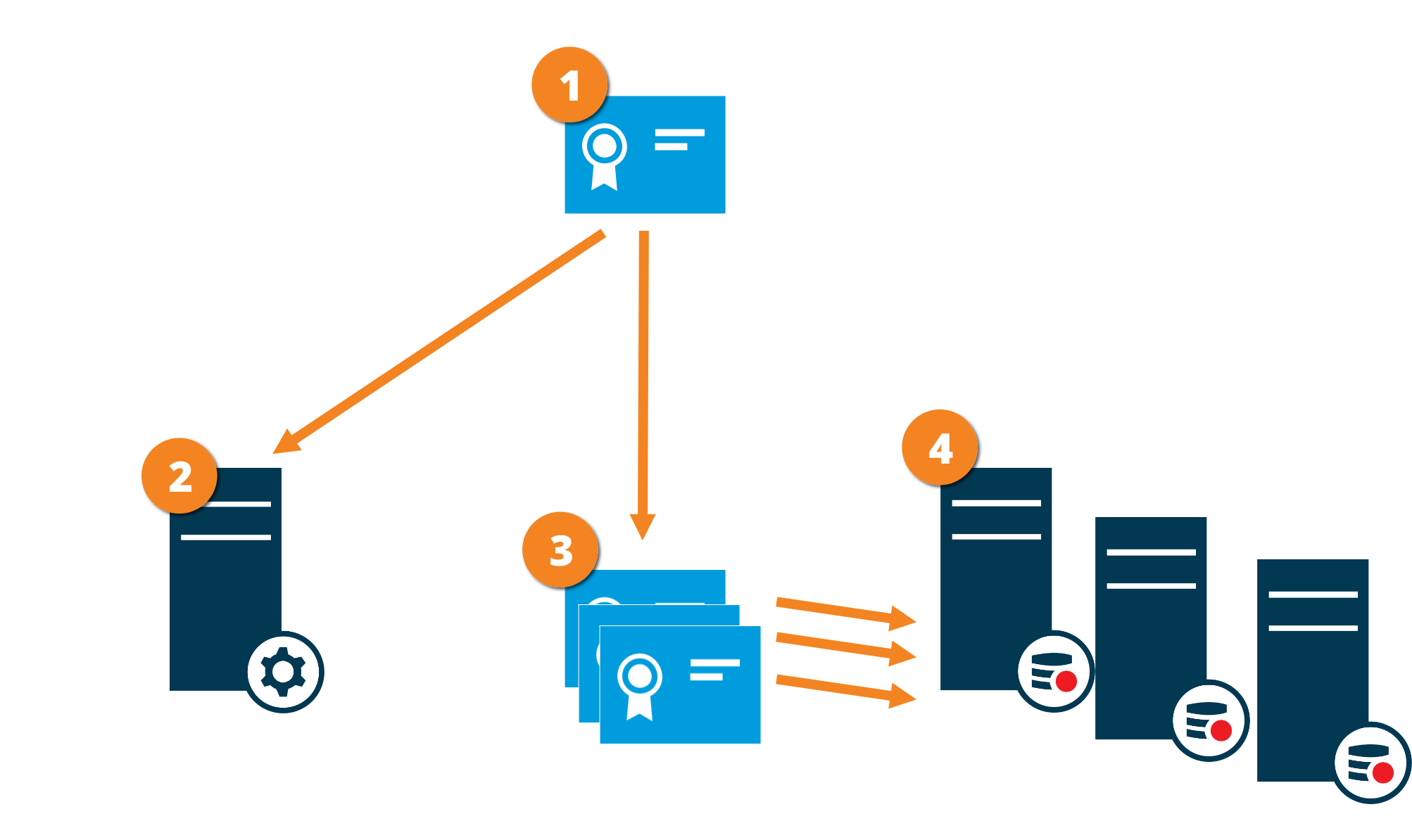
 A CA certificate acts as a trusted third party, trusted by both the Subject/owner (recording server) and by the party that verify the certificate (management server)
A CA certificate acts as a trusted third party, trusted by both the Subject/owner (recording server) and by the party that verify the certificate (management server)
 The public CA certificate must be trusted on the management server. In this way the management server can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA
The public CA certificate must be trusted on the management server. In this way the management server can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA
 The CA certificate is used to issue private server authentication certificates to the recording servers
The CA certificate is used to issue private server authentication certificates to the recording servers
 The created private recording server certificates must be imported to the Windows Certificate Store on the management server
The created private recording server certificates must be imported to the Windows Certificate Store on the management server
Requirements for the private recording server certificate:
- Issued to the recording server so that the recording server's host name is included in the certificate, either as subject (owner) or in the list of DNS names that the certificate is issued to
- Trusted on the management server, by trusting the CA certificate that was used to issue the recording server certificate
- The service account that runs the recording server must have access to the private key of the certificate on the recording server.
Mobile server data encryption (explained)
Sur XProtect VMS, le cryptage est activé ou désactivé par serveur mobile. Lorsque vous activez le cryptage sur un serveur mobile, vous aurez l'option d'utiliser une communication cryptée avec tous les clients, services et intégrations récoltant des flux de données.
Distribution de certificat pour les serveurs mobiles
Le diagramme illustre le concept de base de comment les certificats sont-ils signés, fiables et distribués dans XProtect VMS dans le but de sécuriser la communication avec le serveur mobile.
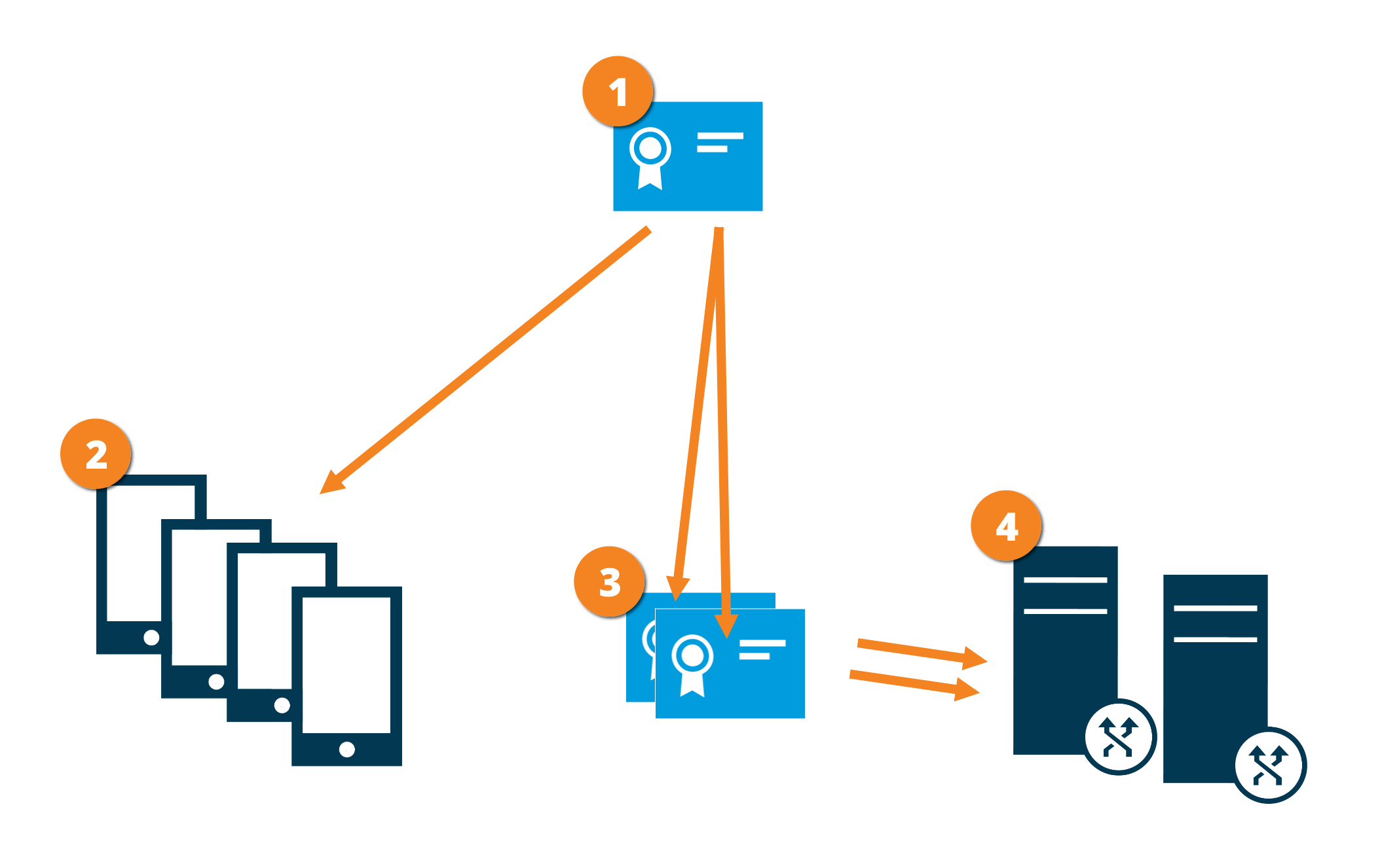
 Un certificat de l'AC agit en tant que tiers de confiance, jouissant de la confiance du sujet/propriétaire (le serveur mobile) et de la partie vérifiant le certificat (tous les clients)
Un certificat de l'AC agit en tant que tiers de confiance, jouissant de la confiance du sujet/propriétaire (le serveur mobile) et de la partie vérifiant le certificat (tous les clients)
 Le certificat privé de l'AC doit être fiable sur tous les clients. De cette manière, les clients vérifient la validité des certificats émis par l'AC
Le certificat privé de l'AC doit être fiable sur tous les clients. De cette manière, les clients vérifient la validité des certificats émis par l'AC
 Le certificat de l'AC est utilisé pour établir une connexion sécurisée entre le serveur mobile et les clients et services
Le certificat de l'AC est utilisé pour établir une connexion sécurisée entre le serveur mobile et les clients et services
 Le certificat de l'AC doit être installé sur un ordinateur exécutant le serveur mobile
Le certificat de l'AC doit être installé sur un ordinateur exécutant le serveur mobile
Prérequis pour le certificat de l'AC :
- Le nom d'hôte du serveur mobile doit être inclus dans le certificat, soit en tant qu'objet/propriétaire ou dans la liste des noms DNS auxquels est émis le certificat
- Un certificat doit être fiable sur tous les périphériques exécutant des services qui collectent des flux de données depuis le serveur mobile
- Le compte du service exécutant le serveur mobile doit avoir accès à la clé privée du certificat de l'AC

