Secure communication (explained)
El Protocolo de Transferencia de Hipertexto Seguro (HTTPS) es una extensión del Protocolo de Transferencia de Hipertexto (HTTP) para la comunicación segura a través de una red informática. En HTTPS, el protocolo de comunicación está cifrado mediante Transport Layer Security (TLS), o su predecesor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL).
En XProtect VMS, la comunicación segura se obtiene utilizando TLS/SSL con cifrado asimétrico (RSA).
TLS/SSL utiliza un par de claves, una privada y otra pública, para autenticar, asegurar y gestionar las conexiones seguras.
Una autoridad de certificación (CA) es cualquiera que pueda emitir certificados raíz. Puede tratarse de un servicio de Internet que emita certificados raíz, o de cualquier persona que genere y distribuya manualmente un certificado. Una CA puede emitir certificados para servicios web, es decir, para cualquier software que utilice la comunicación https. Este certificado contiene dos claves, una clave privada y una clave pública. La clave pública se instala en los clientes de un servicio web (clientes del servicio) mediante la instalación de un certificado público. La clave privada se utiliza para firmar los certificados del servidor que deben instalarse en el mismo. Siempre que un cliente de servicio llama al servicio web, el servicio web envía el certificado del servidor, incluida la clave pública, al cliente. El cliente de servicio puede validar el certificado del servidor utilizando el certificado de CA público ya instalado. El cliente y el servidor pueden ahora utilizar los certificados público y privado del servidor para intercambiar una clave secreta y establecer así una conexión segura TLS/SSL.
Para los certificados distribuidos manualmente, los certificados deben ser instalados antes de que el cliente pueda realizar dicha verificación.
Vea Seguridad de capa de transporte para tener más información sobre TLS.
Los certificados tienen una fecha de caducidad. XProtect VMS no le avisará cuando un certificado esté a punto de caducar. Si un certificado caduca:
• Los clientes dejarán de confiar en el servidor de grabación con el certificado caducado y, por tanto, no podrán comunicarse con él
• Los servidores de grabación dejarán de confiar en el servidor de gestión con el certificado caducado y, por tanto, no podrán comunicarse con él
• Los dispositivos móviles dejarán de confiar en el servidor móvil con el certificado caducado y, por tanto, no podrán comunicarse con él
Para renovar los certificados, siga los pasos de esta guía como lo hizo cuando creó los certificados.
Management server encryption (explained)
You can encrypt the two-way connection between the management server and the recording server. When you enable encryption on the management server, it applies to connections from all the recording servers that connect to the management server. If you enable encryption on the management server, you must also enable encryption on all of the recording servers. Before you enable encryption, you must install security certificates on the management server and all recording servers.
Certificate distribution for management servers
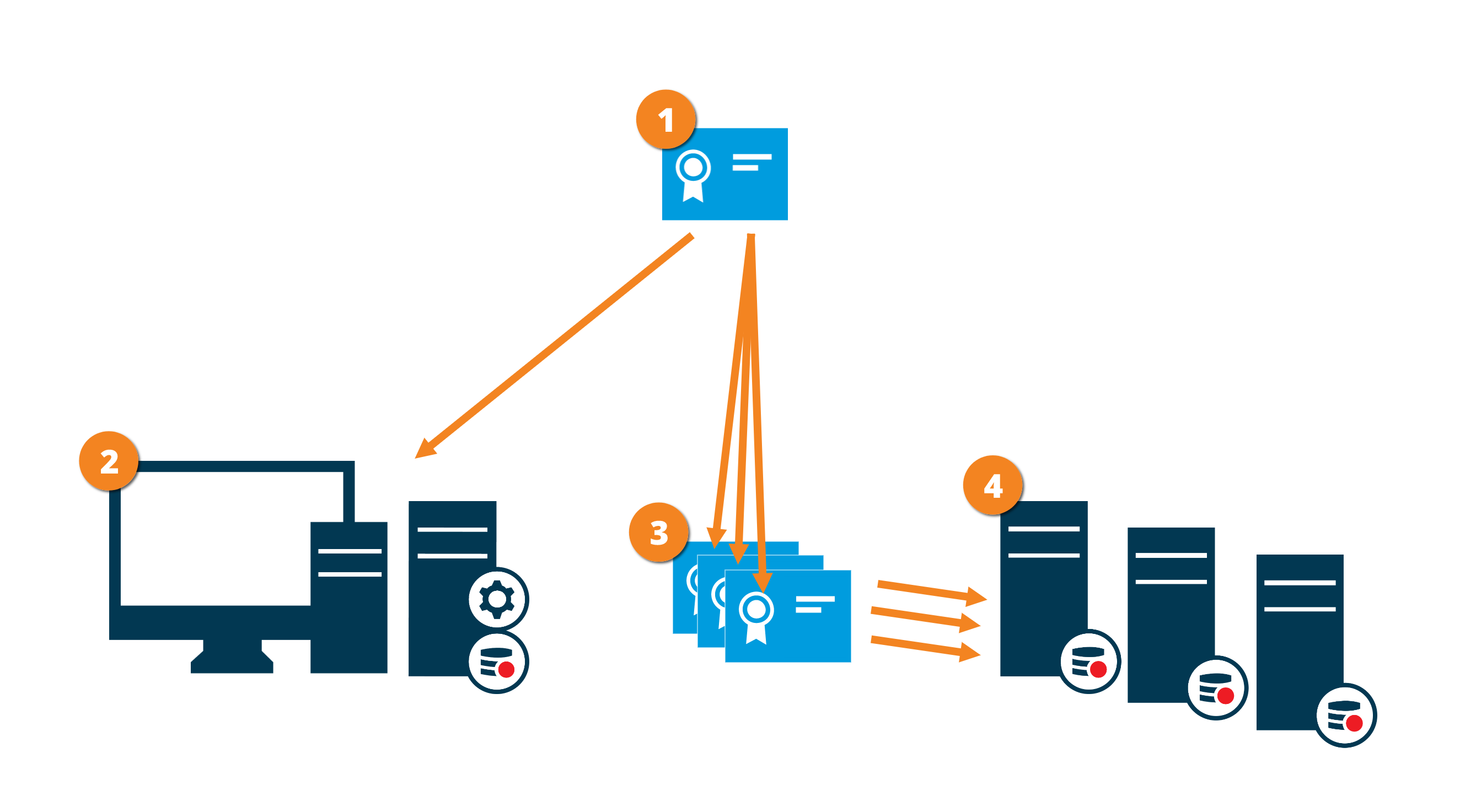
The graphic illustrates the basic concept of how certificates are signed, trusted, and distributed in XProtect VMS to secure the communication to the management server.
 A CA certificate acts as a trusted third party, trusted by both the subject/owner (management server) and by the party that verifies the certificate (recording servers)
A CA certificate acts as a trusted third party, trusted by both the subject/owner (management server) and by the party that verifies the certificate (recording servers)
 The CA certificate must be trusted on all recording servers. In this way, the recording servers can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA
The CA certificate must be trusted on all recording servers. In this way, the recording servers can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA
 The CA certificate is used to establish a secure connection between the management server and the recording servers
The CA certificate is used to establish a secure connection between the management server and the recording servers
 The CA certificate must be installed on the computer on which the management server is running
The CA certificate must be installed on the computer on which the management server is running
Requirements for the private management server certificate:
- Issued to the management server so that the management server's host name is included in the certificate, either as subject (owner) or in the list of DNS names that the certificate is issued to
- Trusted on the management server itself, by trusting the CA certificate that was used to issue the management server certificate
- Trusted on all recording servers connected to the management server by trusting the CA certificate that was used to issue the management server certificate
Recording server data encryption (explained)
Encryption to clients and servers that retrieve data from the recording server
When you enable encryption on a recording server, communication to all clients, servers, and integrations that retrieve data streams from the recording server are encrypted. In this document referred to as 'clients':
- XProtect Smart Client
- Management Client
- Management Server (for System Monitor and for images and AVI video clips in email notifications)
- XProtect Mobile Server
- XProtect Event Server
- XProtect LPR
- Milestone Open Network Bridge
- XProtect DLNA Server
- Sites that retrieve data streams from the recording server through Milestone Interconnect
- Some third-party MIP SDK integrations
Certificate distribution
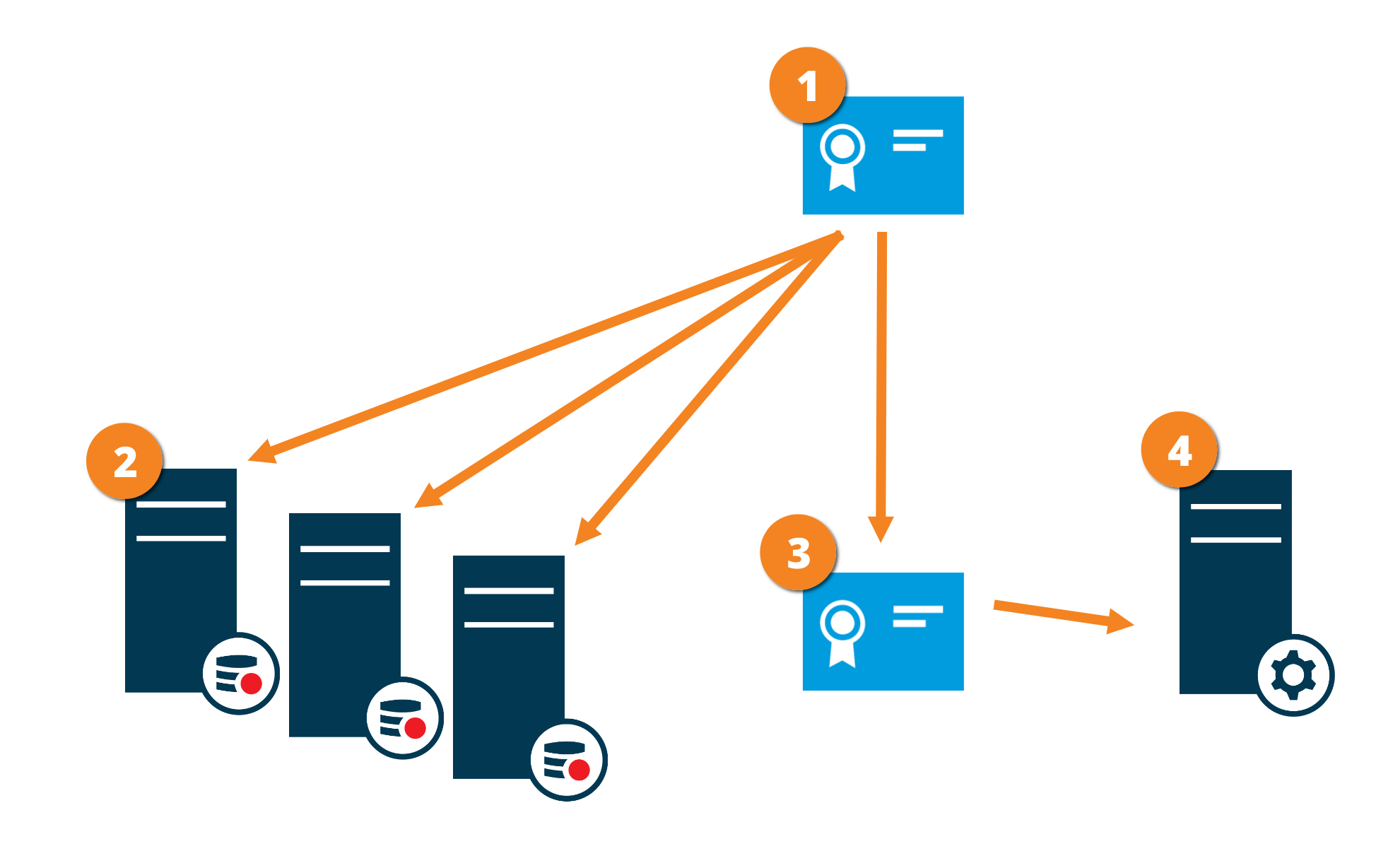
The graphic illustrates the basic concept of how certificates are signed, trusted, and distributed in XProtect VMS to secure the communication to the recording server.
 A CA certificate acts as a trusted third-party, trusted by both the Subject/owner (recording server) and by the party that verify the certificate (clients)
A CA certificate acts as a trusted third-party, trusted by both the Subject/owner (recording server) and by the party that verify the certificate (clients)
 The public CA certificate must be trusted on all client computers. In this way the clients can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA
The public CA certificate must be trusted on all client computers. In this way the clients can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA
 The CA certificate is used to issue private server authentication certificates to the recording servers
The CA certificate is used to issue private server authentication certificates to the recording servers
 The created private recording server certificates must be imported to the Windows Certificate Store on all recording servers
The created private recording server certificates must be imported to the Windows Certificate Store on all recording servers
Requirements for the private recording server certificate:
- Issued to the recording server so that the recording server's host name is included in the certificate, either as subject (owner) or in the list of DNS names that the certificate is issued to
- Trusted on all computers running services that retrieve data streams from the recording servers, by trusting the CA certificate that was used to issue the recording server certificate
- The service account that runs the recording server must have access to the private key of the certificate on the recording server.
If you enable encryption on the recording servers and your system applies failover recording servers, Milestone recommends that you also prepare the failover recording servers for encryption.
Encryption from the management server
You can encrypt the two-way connection between the management server and the recording server. When you enable encryption on the management server, it applies to connections from all the recording servers that connect to the management server. Therefore, you need to enable encryption on all the recording servers. Before you enable encryption, you must install security certificates on the management server and all recording servers.
Certificate distribution
The graphic illustrates the basic concept of how certificates are signed, trusted, and distributed in XProtect VMS to secure the communication from the management server.
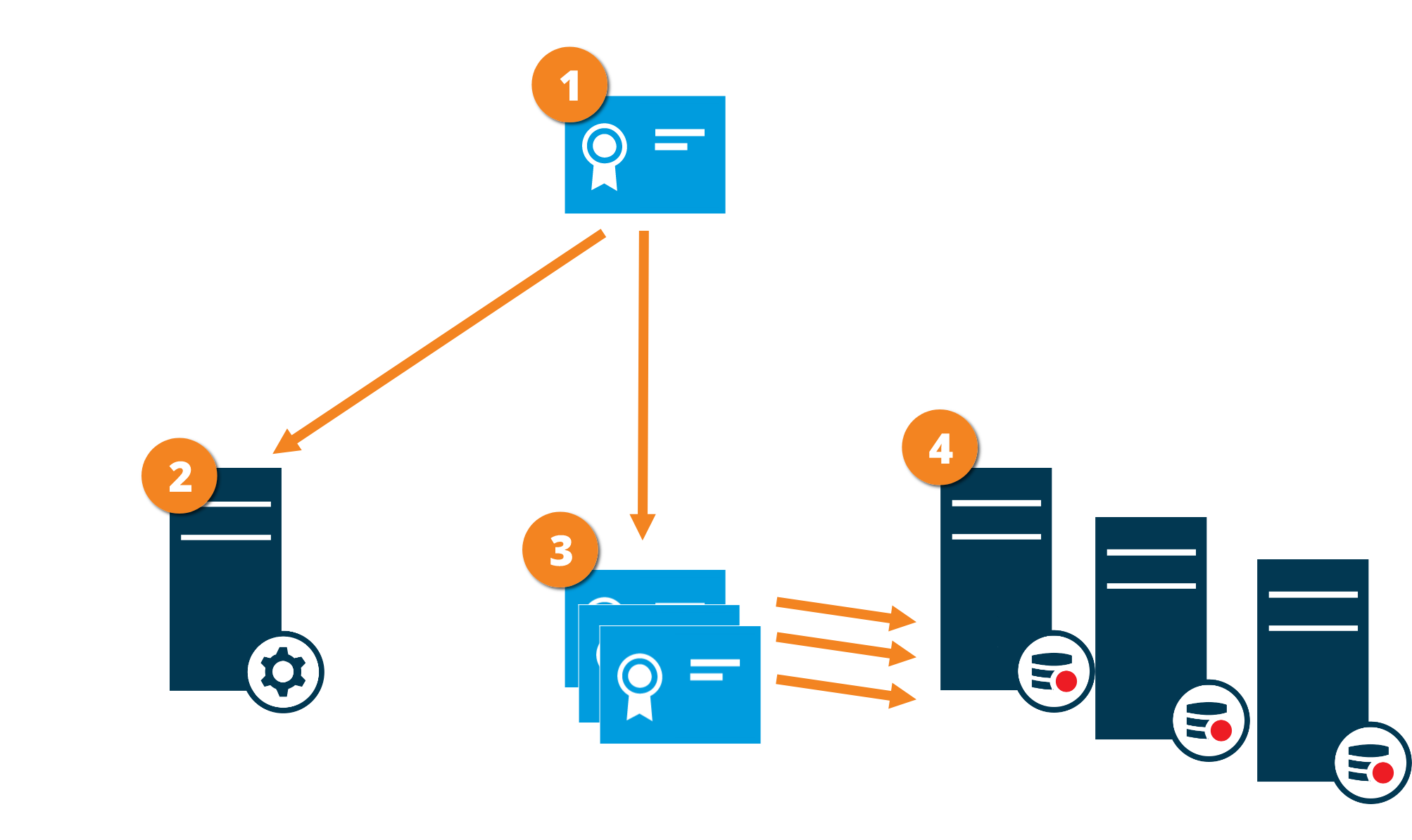
 A CA certificate acts as a trusted third party, trusted by both the Subject/owner (recording server) and by the party that verify the certificate (management server)
A CA certificate acts as a trusted third party, trusted by both the Subject/owner (recording server) and by the party that verify the certificate (management server)
 The public CA certificate must be trusted on the management server. In this way the management server can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA
The public CA certificate must be trusted on the management server. In this way the management server can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA
 The CA certificate is used to issue private server authentication certificates to the recording servers
The CA certificate is used to issue private server authentication certificates to the recording servers
 The created private recording server certificates must be imported to the Windows Certificate Store on the management server
The created private recording server certificates must be imported to the Windows Certificate Store on the management server
Requirements for the private recording server certificate:
- Issued to the recording server so that the recording server's host name is included in the certificate, either as subject (owner) or in the list of DNS names that the certificate is issued to
- Trusted on the management server, by trusting the CA certificate that was used to issue the recording server certificate
- The service account that runs the recording server must have access to the private key of the certificate on the recording server.
Mobile server data encryption (explained)
En XProtect VMS, el cifrado se habilita o deshabilita por servidor móvil. Al activar el cifrado en un servidor móvil, tendrá la opción de utilizar la comunicación cifrada con todos los clientes, servicios e integraciones que recuperen flujos de datos.
Distribución de certificados para servidores móviles
El gráfico ilustra el concepto básico de cómo se firman, confían y distribuyen los certificados en XProtect VMS para asegurar la comunicación con el servidor móvil.
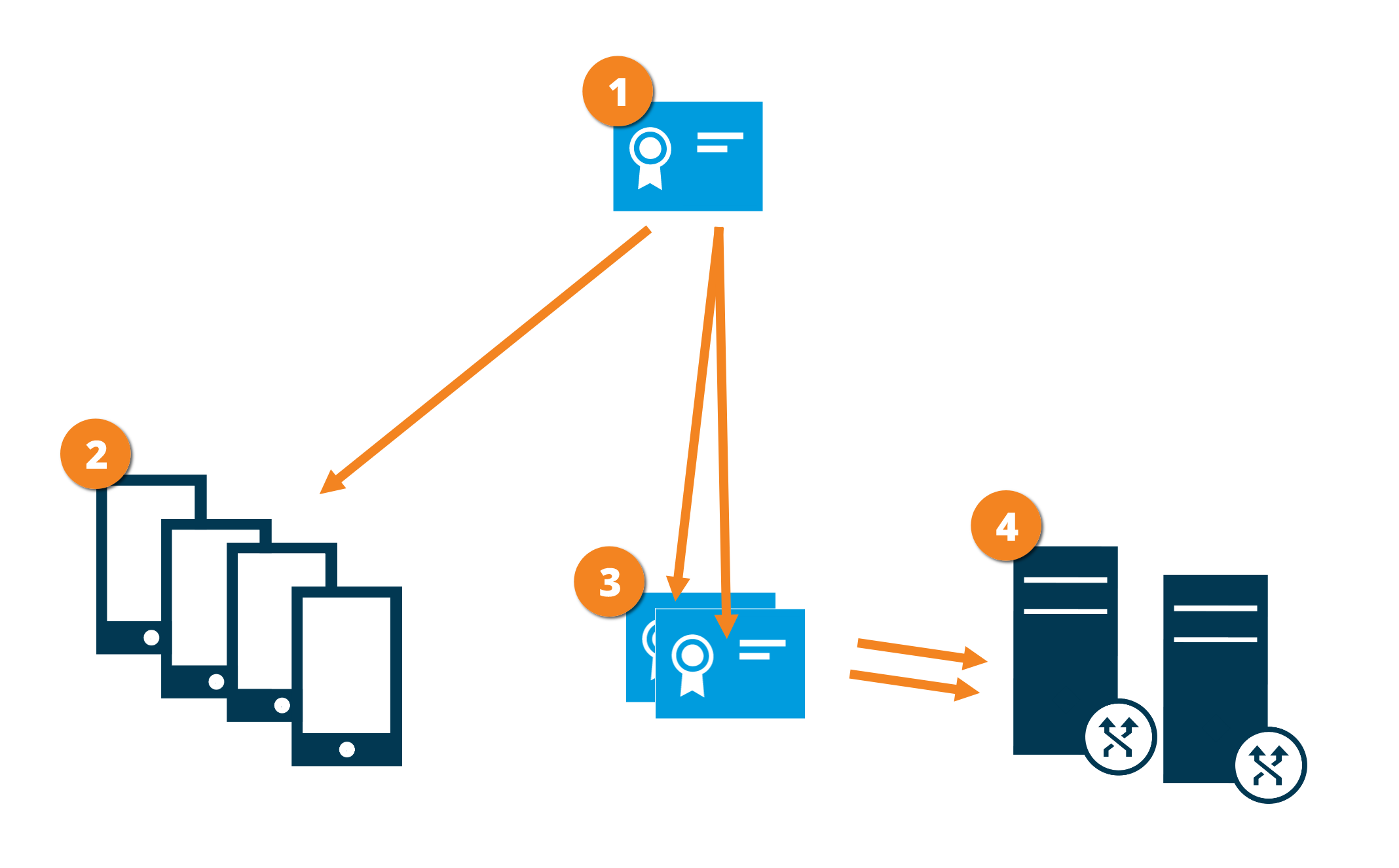
 Un certificado CA actúa como un tercero de confianza, en el que confían tanto el sujeto/propietario (servidor móvil) como la parte que verifica el certificado (todos los clientes)
Un certificado CA actúa como un tercero de confianza, en el que confían tanto el sujeto/propietario (servidor móvil) como la parte que verifica el certificado (todos los clientes)
 El certificado CA debe ser de confianza en todos los clientes. De este modo, los clientes pueden verificar la validez de los certificados emitidos por la CA
El certificado CA debe ser de confianza en todos los clientes. De este modo, los clientes pueden verificar la validez de los certificados emitidos por la CA
 El certificado CA se utiliza para establecer una conexión segura entre el servidor móvil y los clientes y servicios
El certificado CA se utiliza para establecer una conexión segura entre el servidor móvil y los clientes y servicios
 El certificado CA debe estar instalado en el ordenador en el que se está ejecutando el servidor móvil
El certificado CA debe estar instalado en el ordenador en el que se está ejecutando el servidor móvil
Requisitos para el certificado CA:
- El nombre de host del servidor móvil debe estar incluido en el certificado, ya sea como sujeto/propietario o en la lista de nombres DNS a los que se emite el certificado
- El certificado debe ser de confianza en todos los dispositivos que ejecuten servicios que recuperen flujos de datos del servidor móvil
- La cuenta de servicio que ejecuta el servidor móvil debe tener acceso a la clave privada del certificado CA

