Encryption
This section gives you an introduction to encryption and certificates.
XProtect systems support secure communication:
|
From |
To |
|---|---|
| Recording Server |
Management Server |
| Management Server |
Recording Server |
| Clients, servers, and integrations that retrieve data streams from the recording server |
Recording Server |
| Mobile devices | Mobile Server |
| Management Server | Data Collector servers affiliated with remote servers |
| Data Collector servers affiliated with remote servers | Management Server |
When do you need to install certificates?
First, decide whether your system actually needs encrypted communication.
Don't use certificates with recording server encryption if you are using one or more integrations that don't support HTTPS communication. This is, for example, third-part MIP SDK integrations that don't support HTTPS.
Unless your installation is made in a physically isolated network, it's recommended that you secure the communication by using certificates.
This document describes when to use certificates:
- If your XProtect VMS system is set up in a Windows Workgroup environment
- Before you install or upgrade to XProtect VMS 2019 R1 or newer, if you want to enable encryption during the installation
- Before you enable encryption, if you installed XProtect VMS 2019 R1 or newer without encryption
- When you renew or replace certificates due to expiry
Introduction to certificates
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) est une extension de Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) pour une communication sécurisée sur un réseau informatique. Sur HTTPS, le protocole de communication est crypté en utilisant Sécurité de la couche transport (TLS), ou son prédécesseur, Couche de sockets sécurisés (SSL).
Dans XProtect VMS, la communication sécurisée est obtenue en utilisant TLS/SSL avec un chiffrement asymétrique (RSA).
TLS/SSL utilise une paire de clés (une privée, une publique) pour authentifier, sécuriser et gérer les connexions sécurisées.
Une autorité de certification (AC) est toute personne capable d'émettre des certificats racine. Il peut s'agir d'un service Internet qui émet des certificats racine ou de toute personne qui génère manuellement et distribue un certificat. Une AC peut émettre des certificats aux services Web, c'est-à-dire à tout logiciel utilisant la communication https. Ce certificat contient deux clés, une clé privée et une clé publique. La clé publique est installée sur les clients d'un service Web (clients de service) en installant un certificat public. La clé privée est utilisée pour la signature des certificats de serveur qui doivent être installés sur le serveur. Lorsqu'un client de service appelle le service Web, le service Web envoie le certificat du serveur incluant la clé publique au client. Le client de service peut valider le certificat de serveur utilisant le certificat public de l'AC déjà installé. Le client et le serveur peuvent maintenant utiliser les certificats de serveur publics et privés pour échanger une clé secrète et par conséquent, établir une connexion TLS/SSL sécurisée.
Pour les certificats distribués manuellement, les certificats doivent être installés avant que le client ne puisse effectuer cette vérification.
Pour plus d'informations sur TLS : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transport_Layer_Security
In XProtect VMS, the following locations are where you can enable TLS/SSL encryption:
- In the communication between the management server and the recording servers, event servers, and mobile servers
- On the recording server in the communication with clients, servers, and integrations that retrieve data streams from the recording server
- In the communication between clients and the mobile server
Certificate distribution
The graphic illustrates the basic concept of how certificates are signed, trusted, and distributed in XProtect VMS.
 A CA certificate acts as a trusted third-party, trusted by both the Subject/owner (server) and by the party that verifies the certificate (clients).
A CA certificate acts as a trusted third-party, trusted by both the Subject/owner (server) and by the party that verifies the certificate (clients).
 The public CA certificate must be trusted on all client computers. In this way the clients can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA.
The public CA certificate must be trusted on all client computers. In this way the clients can verify the validity of the certificates issued by the CA.
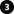 The CA certificate is used to issue private server authentication certificates to the servers.
The CA certificate is used to issue private server authentication certificates to the servers.
 The created private SSL certificates must be imported to the Windows Certificate Store on all servers.
The created private SSL certificates must be imported to the Windows Certificate Store on all servers.
Requirements for the private SSL certificate:
- Issued to the server so that the server's host name is included in the certificate, either as subject (owner) or in the list of DNS names that the certificate is issued to
- Trusted on all computers running services or applications that communicate with the service on the servers, by trusting the CA certificate that was used to issue the SSL certificate
- The service account that runs the server must have access to the private key of the certificate on the server.
Certificates have an expiry date. XProtect VMS will not warn you when a certificate is about to expire. If a certificate expires, the clients will no longer trust the server with the expired certificate and thus cannot communicate with it.
To renew the certificates, follow the steps in this guide as you did when you created certificates.
Pour plus d'informations, voir le guide des certificats sur comment sécuriser votre installation de XProtect VMS.