Site Navigation: Server logs
This article describes how to change log settings, filter logs, and create exports.
Logs (explained)
Logs are a detailed record of user activity, events, actions, and errors in the system.
To see logs, in the Site Navigation pane, select Server Logs.
|
Log type |
What is logged? |
|---|---|
| System logs |
System-related information |
| Audit logs |
User activity |
| Rule-triggered logs |
Rules in which users have specified the Make new <log entry> action. For more information about the <log entry> action, see Actions and stop actions (explained). |
To see logs in a different language, see General tab (options) under Options.
To export logs as comma-separated values (.csv) files, see Export logs.
To change log settings, see Server Logs tab (options).
Filter logs
In each log window, you can apply filters to see log entries from, for example, a specific time span, device, or user.
-
In the Site Navigation pane, select Server Logs. By default, the System logs tab appears.
To navigate between log types, select a different tab.
-
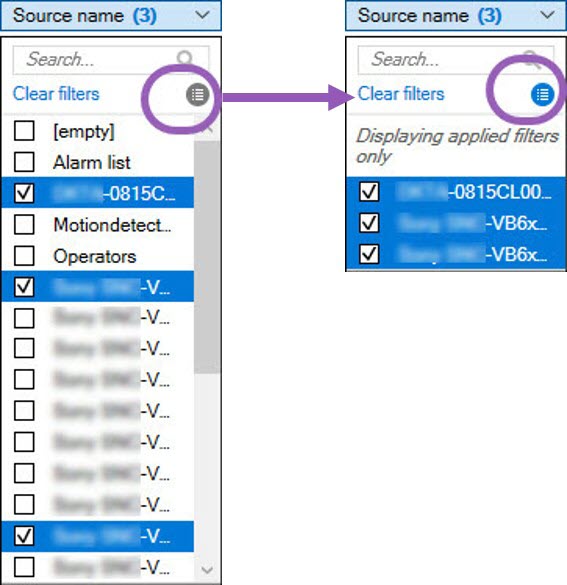
Under the tabs, select a filter group, for example, Category, Source type, or User.

A list of filters appears.
-
Select a filter to apply it. Select the filter again to remove it.
Optional: In a list of filters, select Display applied filters only to see only the filters that you applied.
The contents of your export change depending on the filters that you apply. For information about your export, see Export logs.
Export logs
Exporting logs helps you to, for example, save log entries beyond the log retention period. You can export logs as comma-separated values (.csv) files.
To export a log:
-
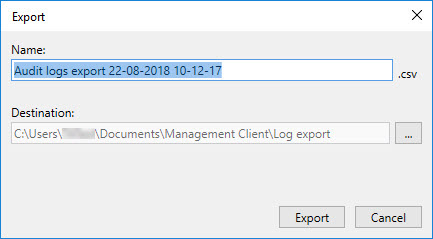
Select Export in the upper-right corner. The Export window appears.
-
In the Export window, in the Name field, specify a name for the log file.
-
By default, exported log files are saved in your Log export folder. To specify a different location, select
 to the right of the Destination field.
to the right of the Destination field. -
Select Export to export the log.
The contents of your export change depending on the filters that you apply. For information about your export, see Filter logs.
Allow 2018 R2 and earlier components to write logs
The 2018 R3 version of the log server introduces authentication for added security. This prevents 2018 R2 and earlier components from writing logs to the new log server.
Affected components:
- XProtect Smart Client
- XProtect LPR Plug-in
- LPR Server
- Access Control Plug-in
- Event Server
- Alarm Plug-in
If you're using the 2018 R2 or earlier version of any of the components listed above, you must decide whether or not to allow the component to write logs to the new log server:
-
Select Tools > Options.
-
In the Options dialog box, at the bottom of the Server Logs tab, find the Allow 2018 R2 and earlier components to write logs check box.
- Select the check box to allow 2018 R2 and earlier components to write logs
- Clear the check box to not allow 2018 R2 and earlier components to write logs
System logs (properties)
Each row in a log represents a log entry. A log entry contains a number of information fields:
|
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
| Log level |
Info, warning, or error. |
| Local time |
Timestamped in the local time of your system's server. |
| Message text |
The identification number for the logged incident. |
| Category | The type of logged incident. |
| Source type |
The type of equipment on which the logged incident occurred, for example, server or device. |
| Source name |
The name of the equipment on which the logged incident occurred. |
| Event type |
The type of event represented by the logged incident. |
Audit logs (properties)
Each row in a log represents a log entry. A log entry contains a number of information fields:
|
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
| Local time |
Timestamped in the local time of your system's server. |
| Message text |
Shows a description of the logged incident. |
| Permission | The information about whether the remote user action was allowed (granted) or not. |
| Category | The type of logged incident. |
| Source type |
The type of equipment on which the logged incident occurred, for example, server or device. |
| Source name |
The name of the equipment on which the logged incident occurred. |
| User |
The user name of the remote user causing the logged incident. |
| User location | The IP address or host name of the computer from which the remote user caused the logged incident. |
Rule-triggered logs (properties)
Each row in a log represents a log entry. A log entry contains a number of information fields:
|
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
| Local time |
Timestamped in the local time of your system's server. |
| Message text |
Shows a description of the logged incident. |
| Category | The type of logged incident. |
| Source type |
The type of equipment on which the logged incident occurred, for example, server or device. |
| Source name |
The name of the equipment on which the logged incident occurred. |
| Event type |
The type of event represented by the logged incident. |
| Rule name | The name of the rule triggering the log entry. |
| Service name | The name of the service on which the logged incident occurred. |
Was this article helpful?
Thanks for your feedback!

